Download this example
Download this example as a Jupyter Notebook or as a Python script.
Parametric differential vias#
This example demonstrates how a differential via pair can be created using the EDB Python interface.
The final differential via pair is shown below.
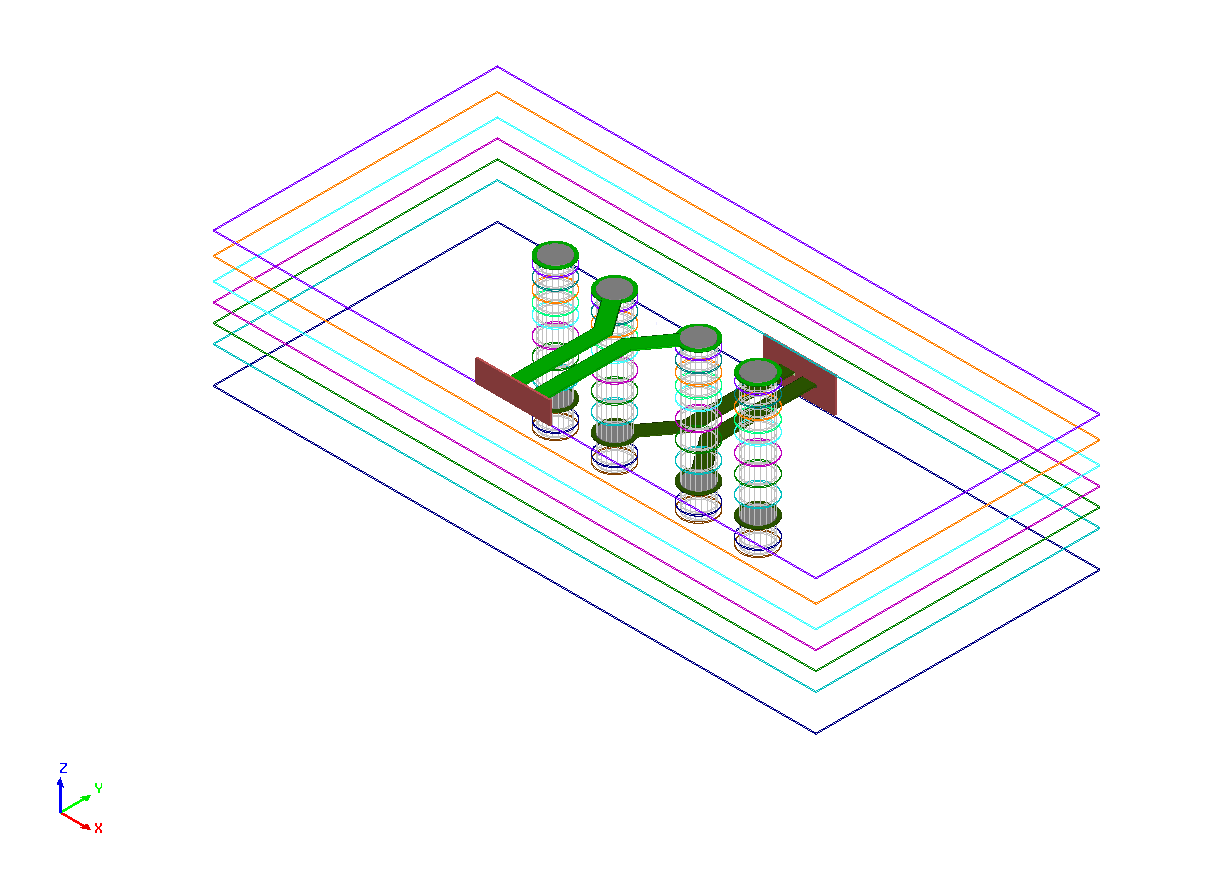
Keywords: Differential Via
Prerequisites#
Perform imports#
[1]:
import os
import tempfile
import pyedb
Define constants#
Constants help ensure consistency and avoid repetition throughout the example.
[2]:
AEDT_VERSION = "2025.1"
NG_MODE = False # Open AEDT UI when it is launched.
[3]:
temp_folder = tempfile.TemporaryDirectory(suffix=".ansys")
Start the EDB#
[4]:
aedb_path = os.path.join(temp_folder.name, "diff_via.aedb")
print(f"AEDB file path: {aedb_path}")
edb = pyedb.Edb(edbpath=aedb_path, edbversion=AEDT_VERSION)
AEDB file path: C:\Users\ansys\AppData\Local\Temp\tmplobplqtw.ansys\diff_via.aedb
PyEDB INFO: Star initializing Edb 03:57:51.423043
PyEDB INFO: Edb version 2025.1
PyEDB INFO: StdOut is enabled
PyEDB INFO: Logger is initialized in EDB.
PyEDB INFO: legacy v0.54.0
PyEDB INFO: Python version 3.10.11 (tags/v3.10.11:7d4cc5a, Apr 5 2023, 00:38:17) [MSC v.1929 64 bit (AMD64)]
PyEDB INFO: EDB C:\Users\ansys\AppData\Local\Temp\tmplobplqtw.ansys\diff_via.aedb created correctly.
PyEDB INFO: EDB initialized.Time lapse 0:00:09.635292
Model Creation#
Add stackup layers#
A stackup can be created layer by layer or imported from a configuration file.
[5]:
edb.stackup.add_layer("GND")
edb.stackup.add_layer("Diel", "GND", layer_type="dielectric", thickness="0.1mm", material="FR4_epoxy")
edb.stackup.add_layer("TOP", "Diel", thickness="0.05mm")
[5]:
<pyedb.dotnet.database.edb_data.layer_data.StackupLayerEdbClass at 0x27d79009660>
Create signal nets and ground planes#
Create a signal net and ground planes.
[6]:
points = [[0.0, 0], [100e-3, 0.0]]
edb.modeler.create_trace(points, "TOP", width=1e-3)
points = [[0.0, 1e-3], [0.0, 10e-3], [100e-3, 10e-3], [100e-3, 1e-3], [0.0, 1e-3]]
edb.modeler.create_polygon(points, "TOP")
points = [[0.0, -1e-3], [0.0, -10e-3], [100e-3, -10e-3], [100e-3, -1e-3], [0.0, -1e-3]]
edb.modeler.create_polygon(points, "TOP")
[6]:
<pyedb.dotnet.database.edb_data.primitives_data.EdbPolygon at 0x27d7ca30e50>
Place vias#
[7]:
edb.padstacks.create("MyVia")
edb.padstacks.place([5e-3, 5e-3], "MyVia")
edb.padstacks.place([15e-3, 5e-3], "MyVia")
edb.padstacks.place([35e-3, 5e-3], "MyVia")
edb.padstacks.place([45e-3, 5e-3], "MyVia")
edb.padstacks.place([5e-3, -5e-3], "MyVia")
edb.padstacks.place([15e-3, -5e-3], "MyVia")
edb.padstacks.place([35e-3, -5e-3], "MyVia")
edb.padstacks.place([45e-3, -5e-3], "MyVia")
PyEDB INFO: Padstack MyVia create correctly
[7]:
<pyedb.dotnet.database.edb_data.padstacks_data.EDBPadstackInstance at 0x27d7ca31330>
View the nets#
[8]:
edb.nets.plot(None, color_by_net=True)
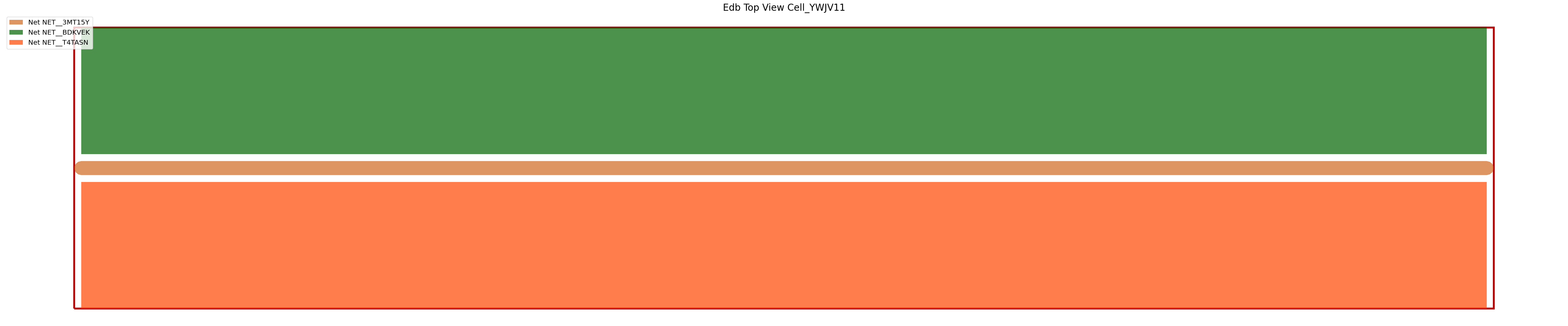
PyEDB INFO: Plot Generation time 0.391
[8]:
(<Figure size 6000x3000 with 1 Axes>,
<Axes: title={'center': 'Edb Top View Cell_GPYTFU'}>)
View the stackup#
[9]:
edb.stackup.plot(plot_definitions="MyVia")
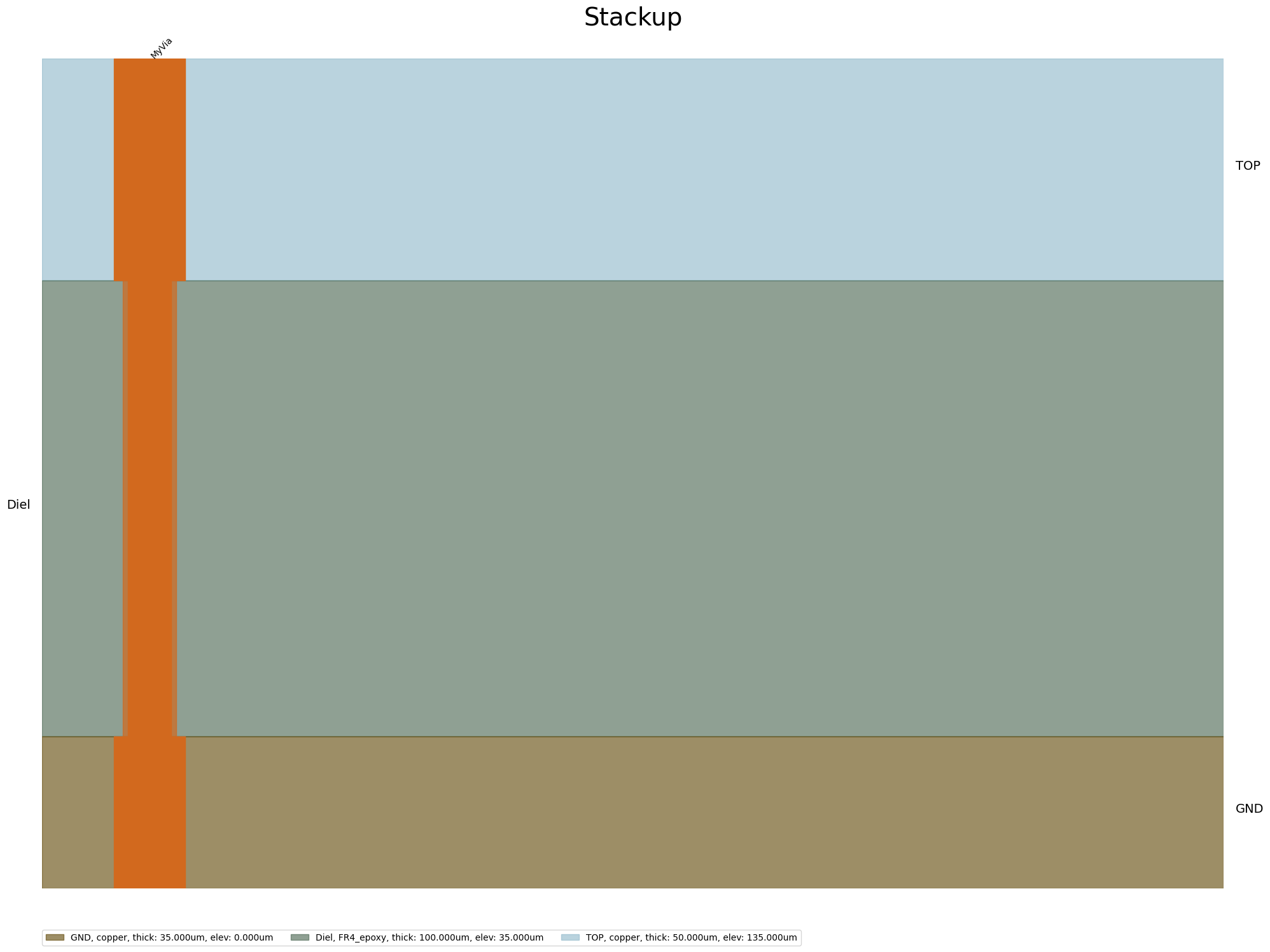
[9]:
<module 'matplotlib.pyplot' from 'C:\\actions-runner\\_work\\pyaedt-examples\\pyaedt-examples\\.venv\\lib\\site-packages\\matplotlib\\pyplot.py'>
Finish#
Save the project#
Save and close EDB.
[10]:
if edb:
edb.save_edb()
edb.close_edb()
print("EDB saved correctly to {}. You can import in AEDT.".format(aedb_path))
PyEDB INFO: EDB file save time: 0.00ms
PyEDB INFO: EDB file release time: 15.63ms
EDB saved correctly to C:\Users\ansys\AppData\Local\Temp\tmplobplqtw.ansys\diff_via.aedb. You can import in AEDT.
Clean up#
All project files are saved in the folder temp_folder.name. If you’ve run this example as a Jupyter notebook, you can retrieve those project files. The following cell removes all temporary files, including the project folder.
[11]:
temp_folder.cleanup()
Download this example
Download this example as a Jupyter Notebook or as a Python script.
